
Submitting a manuscript to an academic journal is a big step. It is also the beginning of a complex publication process in which a manuscript goes through different stages. In each stage, the status of a manuscript changes. Understanding this process is pivotal for academic researchers.
Contents
- Overview of stages when publishing a manuscript
- The meaning of ‘manuscript submitted’
- The meaning of ‘manuscript under consideration’
- The meaning of ‘manuscript under review’
- The meaning of ‘manuscript accepted’
- The meaning of ‘article forthcoming’
- The meaning of ‘article in press’
- FAQs on the status of manuscripts
Overview of stages when publishing a manuscript
Most academic journals use online systems, such as Manuscript Central™, to manage the submission and peer review of articles. These systems also tend to indicate the stage or status of a manuscript.
Academic researchers with little publishing experience may be confused when they see their manuscripts’ (changing) status. But with a bit of information, manuscript stages are quite easy to understand.
A good understanding of the different stages a manuscript goes through during the publication process provides academic researchers with peace of mind. Furthermore, it allows them to correctly indicate the status of their manuscripts, for instance on their academic CV.
Not every journal indicates the same stages. However, the general ‘road’ from a submitted manuscript to a published academic article looks as follows:
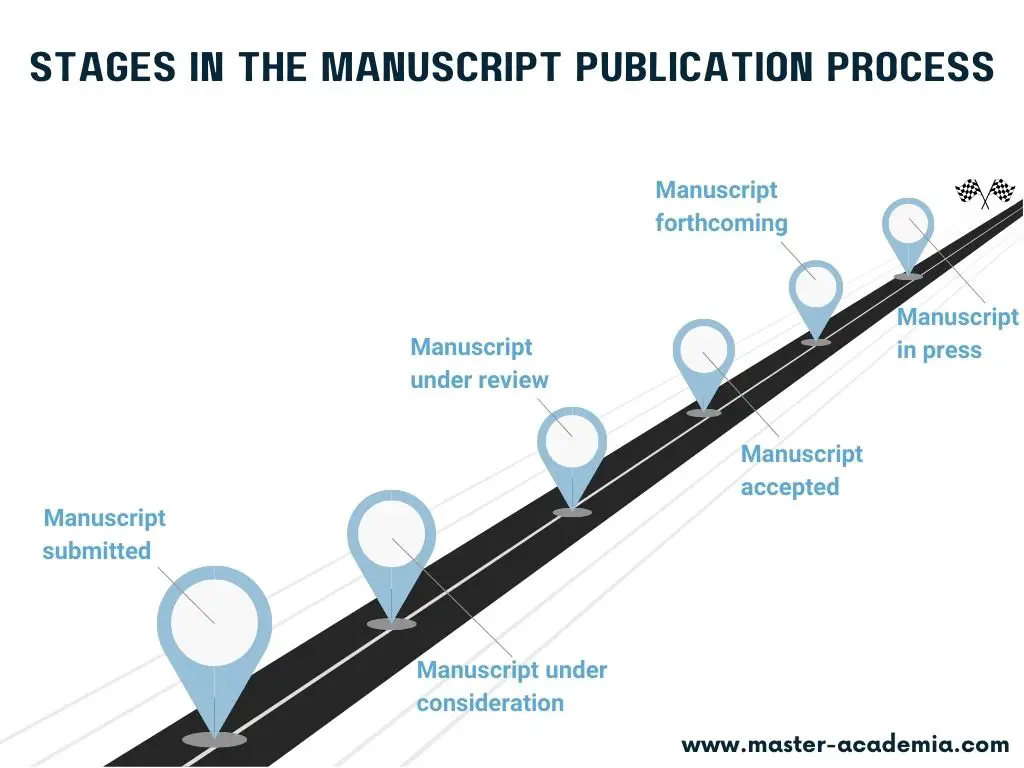
In reality, this ‘road’ or manuscript publication process is not as linear as illustrated in the figure above. A manuscript under consideration can be, for instance, desk-rejected by a journal editor. This means that authors will have to start again and submit their manuscripts to a different journal.
A manuscript may also not pass the peer review stage or may have to undergo several rounds of revisions before it is finally accepted.
Therefore, it is crucial to consistently present your best work when submitting a manuscript to a journal. This entails thorough editing. Professional publication support, such as the services provided by Editage, can greatly enhance your chances of acceptance. You can receive a 30% discount on their services if you sign up via Master Academia.
The meaning of ‘manuscript submitted’
When a manuscript is ‘submitted’, it means that the manuscript has been sent to an academic journal to be considered for publishing. Most journals use online systems to administer submissions and to convey assessments and reviews of the manuscript to its author/s.
After submitting a manuscript, authors usually receive an email from the journal confirming the receipt of the submission. If not, it may be worth sending a short email to the journal editor or editorial assistant just to double-check.
Many online submission systems allow authors to log in via their ORCID IDs, which makes the process more efficient: with an ORCID ID, there is no need to set up new usernames and passwords for every single journal.
The meaning of ‘manuscript under consideration’
For some journals, briefly after submission, the status of a manuscript changes to ‘under consideration’. A manuscript ‘under consideration’ means that one of the journal’s editors is assessing whether the manuscript fulfils all requirements and could be a good fit for the journal thematically.
Therefore, exploring journals’ aims and scopes is a fundamental step when selecting a journal for publication.
A manuscript under consideration indicates a different stage than peer review. Finding good peer reviewers can be challenging. Therefore, journal editors do not send all submitted manuscripts to peer reviewers. Instead, they often have a quick look at submissions themselves, before deciding whether manuscripts qualify for peer review or not.
The meaning of ‘manuscript under review’
When a manuscript is ‘under review’, it has been sent to external peer reviewers and the journal editor awaits these peer reviewers’ assessments. This stage is often the longest one in the manuscript publication process. It can last from a few weeks to several months.
Thus, when the status of a manuscript is ‘under review’, authors have to be patient! That said, if they have not heard back from the journal after several months, it is perfectly fine to send a friendly email to ask for a status update on the peer review process.
You may also like: Types of editorial decisions after peer review (+ how to react)
The meaning of ‘manuscript accepted’
Once journal editors receives the assessment of external peer reviewers, they decide whether or not to accept the manuscript for publication. When a manuscript status changes to ‘accepted’, it means that it will most likely be published in the academic journal.
However, there can be caveats. Manuscripts can be accepted with major or minor revisions, which – at times – require substantial changes. And even if a manuscript is accepted with minor revisions, a journal can still refuse to ultimately publish it.
A ‘manuscript accepted’ is a huge reason to celebrate! In most cases, ‘accepted’ manuscripts will result in a published journal article. However, it is good to be aware that journals have no legal obligation to publish manuscripts, even if their status is ‘accepted’.
The meaning of ‘article forthcoming’
When a manuscript or article is indicated as ‘forthcoming’, it means that it has been accepted by a journal for publication and that the authors wait for the production process to start.
Despite a publishing agreement between authors and journal editors, manuscripts are not always published immediately. Sometimes, the journal waits until more articles are accepted so that they can be compiled in an issue. Other times, it simply takes some time for the production process to start.
The difference between ‘accepted’ and ‘forthcoming’
The difference between an accepted and a forthcoming academic article is often unclear, and many academic researchers use these status indications interchangeably. However, when an article is ‘forthcoming’, it generally means that all required manuscript revisions are completed and approved by the journal editor/s. ‘Accepted’ manuscripts, on the other hand, can still undergo changes.
The meaning of ‘article in press’
The last bit of uncertainty of whether a manuscript will be published or not disappears when an article is ‘in press’. When an article is ‘in press’, it is in the production stage in which the journal administers final formatting, spelling and reference checks.
The difference between ‘accepted’ and ‘in press’
The difference between a manuscript that has been ‘accepted’ and a manuscript ‘in press’ is the certainty of the latter that it will result in a publication. An ‘accepted manuscript’ still runs the risk of not resulting in a journal publication, albeit a very small one. When an article is ‘in press’, its publication is certain and just a matter of administration. This administration tends to take less than two weeks.
The difference between ‘forthcoming’ and ‘in press’
The difference between a ‘forthcoming’ article and an article ‘in press’ is very small, and the status descriptions are often used interchangeably. ‘In press’ tends to have a stronger connotation to the final production stage in the publication process, which means that the published articles can be expected within a matter of days or several weeks at most. A ‘forthcoming’ article, however, may take longer to be published.
FAQs on the status of manuscripts
Do I include submitted articles on my academic CV?
It is not common practice to include submitted manuscripts on academic CVs. However, as publication processes can be lengthy, listing submitted manuscripts can be useful for some researchers. Early career researchers with few publications to their name, for example, can benefit from showcasing their submitted articles to highlight their (future) research potential. If the decision is made to include submitted articles on an academic CV, it is very important to clearly indicate their status by separating them from *real* publications with a separate headline.
Do I include accepted articles on my academic CV?
It is common practice to include accepted articles on academic CVs, as the likelihood of publication of accepted articles is very high. That said, it is very important to indicate the status of accepted manuscripts correctly. It should be crystal clear if listed articles are not published yet.
How do I know the current status of my manuscript?
The current status of a manuscript can usually be found in the online submission system of the journal. If the online system does not provide any information on the manuscript status, or if the journal does not use online system, authors can send an email to the journal to inquire about the manuscript status. However, it is good to be patient and not advised to contact the journal already a week or two after submitting a manuscript.
Can I contact the journal editor about the status of my manuscript?
It is absolutely legitimate to contact the journal editor and ask about the status of a manuscript. However, it is important to keep in mind that the publication process (and particularly the peer review stage) can take a long time. Therefore, is advised to wait around three months before asking a journal for a status update.



