Systematic literature reviews may seem daunting at first, but they offer substantial benefits, especially in enhancing the theoretical framework for your research! Learn more about systematic literature reviews and their benefits. And have a look at a simple step-by-step guide that breaks down the daunting task of conducting a systematic literature review into simple, actionable steps.
Contents
- What is a systematic literature review?
- The difference between a systematic and a regular literature review
- The difference between a systematic literature review and a meta-analysis
- Benefits of conducting a systematic literature review
- Academic citation databases suitable for systematic literature reviews
- Step-by-step guide for conducting a systematic literature review
What is a systematic literature review?
Systematic literature reviews are a means to rigorously review existing literature on a specific topic. They collect and analyze existing literature in a systematic and replicable way.
Following the definition of a topic of interest and concrete research question, a systematic literature review starts by defining several keywords. Then, academic citation databases are used to retrieve all articles that include these keywords.
Furthermore, inclusion and exclusion criteria for sorting through the existing literature are set up. Think of a time frame, the type of publication (articles, books etc.), a geographic focus, and a disciplinary background. You name it.
Systematic literature reviews are a means to rigorously review existing literature on a specific topic. They collect and analyse existing literature in a systematic and replicable way.
Following the definition of a topic of interest and concrete research question, a systematic literature review starts by defining several keywords. Then, academic citation databases are used to retrieve all articles that include these keywords.
While systematic literature reviews require a lot of work, they can convincingly draw conclusions on the state of the art of existing knowledge, uncover research gaps, and support the creation of new theoretical and conceptual frameworks.
In a systematic literature review, inclusion and exclusion criteria for sorting through the existing literature are set up. Think of a time frame, the type of publication (articles, books etc.), a geographic focus, and a disciplinary background.
Therefore, systematic literature reviews are crystal clear about the process of collecting and analyzing literature, which makes them replicable.
The difference between a systematic and a regular literature review
Before starting to consider whether a systematic literature review is right for you, it is important to be aware of the main differences between systematic and regular literature reviews.
The main differences between a systematic and a regular literature review are the process of collecting and analyzing literature, the accuracy of claims, the scope and replicability.
In a regular literature review, authors select articles or other publications ad hoc, to support the arguments of their work. Authors make claims about the state of the art of academic knowledge on a specific topic, but do not necessarily provide systematic evidence to support their claims.
Therefore, the level of accuracy differs in systematic and regular literature reviews.
Furthermore, authors doing regular literature reviews generally do not explain how they conducted their review, and how they selected relevant literature. Therefore, regular literature reviews are usually not replicable, whereas systematic ones are.
Additionally, the scope of a review differs immensely between systematic and regular literature reviews.
Systematic literature reviews tend to methodically analyze hundreds of articles, whereas regular literature reviews are much more limited in scope and highly selective in their choice of publications that are included.
The difference between a systematic literature review and a meta-analysis
Systematic literature reviews and meta-analyses are frequently confused or used interchangeably, but it’s important to understand that they are distinct methodologies.
While a meta-analysis focuses on synthesizing data and drawing broad conclusions from multiple studies, a systematic literature review is geared towards answering a well-defined research question with a comprehensive and methodical approach.
A meta-analysis involves the comprehensive analysis of results from multiple studies on a particular topic, aiming to identify patterns and draw generalized conclusions. These analyses often rely on statistical methods to combine data from various sources.
On the other hand, systematic literature reviews can take either a qualitative or quantitative approach. They are designed to address a specific and often novel research question, going beyond a mere summary of existing studies.
Benefits of conducting a systematic literature review
Conducting a ‘regular’ literature review is perfectly valid, but there are compelling reasons to consider a systematic literature review for certain research endeavors.
One primary advantage of a systematic review is its ability to address the overwhelming volume of relevant literature that can leave researchers, particularly master’s and PhD students, feeling daunted and unsure of when to stop searching for more material.
By conducting a systematic review, all pertinent literature can be analyzed within specific parameters, alleviating concerns about potentially missing critical information.
Moreover, a systematic literature review offers the advantage of identifying and showcasing research gaps, bolstering the academic significance of one’s work. This comprehensive approach to reviewing existing literature contributes to a stronger foundation for the research and its potential impact.
Additionally, by being transparent and explicit about the methodology employed in collecting and analyzing the literature, researchers enhance the credibility and reliability of their statements and arguments. This explicitness reinforces the trustworthiness of the research findings, which is crucial in the academic world.
Academic citation databases suitable for systematic literature reviews
To conduct systematic literature reviews, it is recommended to utilize a citation database that provides built-in features to refine search queries effectively.
Google Scholar is a widely used search engine among scholars, but its sidebar for limiting search queries is relatively basic. Despite this limitation, the advantage of using Google Scholar is that it is freely accessible to all users, including those without institutional affiliations.
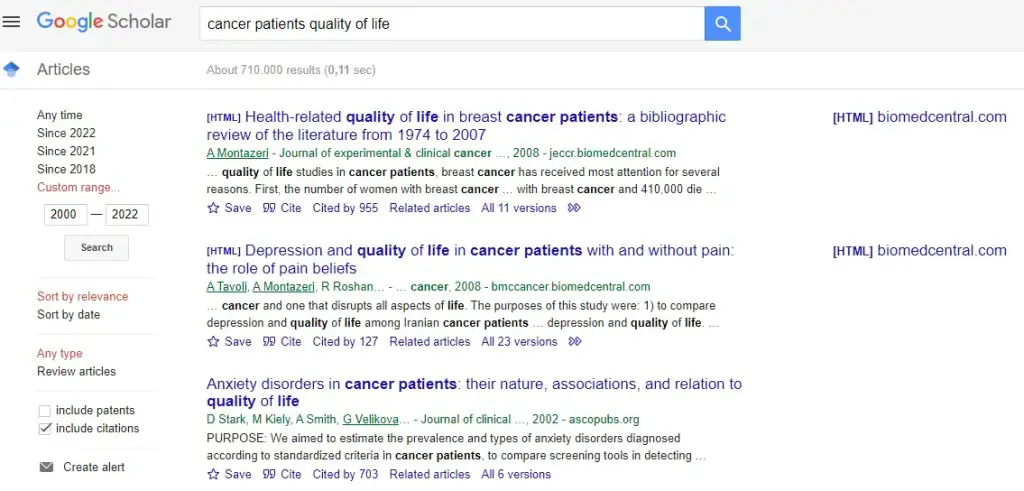
Google Scholar to conduct a systematic literature review
Web of Science to conduct a systematic literature review
Web of Science has very elaborate search options. The search engine allows you to choose from various databases and indexes, such as the Science Citation Index or the Social Science Citation Index. Additionally, it enables you to search for keywords within topics or titles, as well as author names, affiliations, publication years, and more.
Web of Science provides a wide range of Booleans (depicted in the image below on the right) that you can utilize to precisely specify your search criteria. Booleans are a system of logic employed in programming and computer sciences, featuring operators like “AND,” “OR,” and “NOT.” By using these operators, you can fine-tune your search queries and filter results to precisely match what you are looking for.
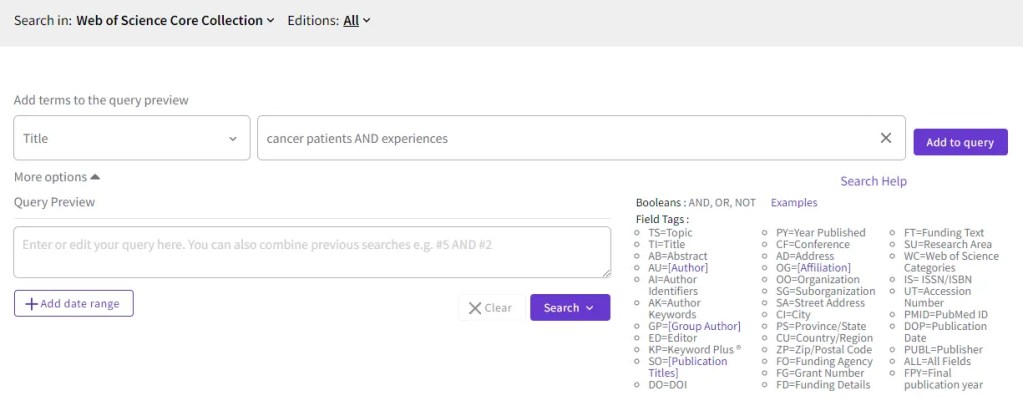
After obtaining search results on Web of Science, you have the option to further refine and organize them based on various criteria, such as research areas, disciplines, languages, regions, document types, and more.
Although it may require some time and practice to become proficient in developing precise search queries on Web of Science, the database offers tremendous opportunities for conducting systematic literature reviews. Its extensive filtering and organizing features empower researchers to gather comprehensive and relevant literature on specific topics.
Scopus to conduct a systematic literature review
Scopus the citation database by publisher Elsevier, boasts access to over 36,000 journals. Its layout and search options closely resemble those of Web of Science, making it a highly recommended platform to explore for research purposes. If you are familiar with Web of Science, you will find Scopus user-friendly and worthwhile to explore for comprehensive academic content.
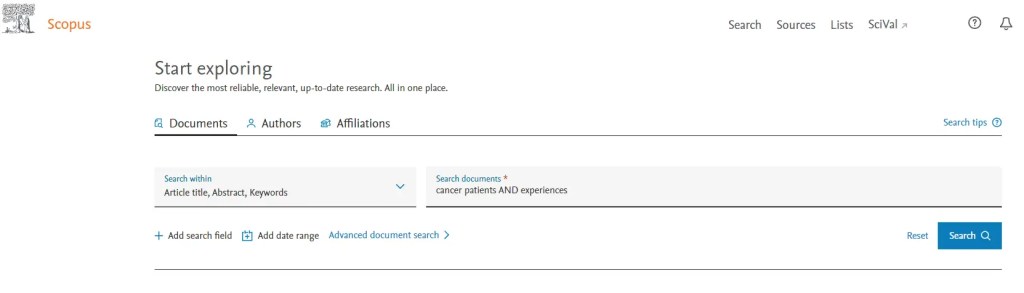
Citation databases can be utilized in combination for more comprehensive research. It is recommended to begin with popular ones like Web of Science and Scopus, as they provide extensive coverage. However, using additional databases can serve as a valuable double-check to ensure no relevant entries are overlooked. Employing multiple databases enhances the likelihood of capturing a comprehensive range of scholarly materials for your research.
Step-by-step guide for conducting a systematic literature review
While each systematic literature review is unique, there are commonly followed steps that serve as a foundation for the process:
- Clearly define a focused and narrow research question.
- Identify relevant keywords to lead you to articles that can potentially answer your research question.
- Choose a suitable citation database and establish inclusion and exclusion criteria, considering factors like timeframe, discipline, journal, research area, and geographical context.
- Download all pertinent results, which may amount to hundreds of articles.
- Systematically screen all titles and abstracts, manually excluding irrelevant articles based on your criteria.
- Create your own database, such as using Excel, to store the remaining entries and read them more thoroughly.
- Categorize the entries and/or their content in a way that provides meaningful insights to answer your research question.
- Develop visual representations like graphs and tables to present your results.
- Write a concise and engaging presentation of your findings, summarizing the key outcomes of the systematic review.
Following these steps will help you conduct a thorough and well-organized systematic literature review.